我们还记得,可以使用诸如 new F() 这样的构造函数来创建一个新对象。
如果 F.prototype 是一个对象,那么 new 操作符会使用它为新对象设置 [[Prototype]]。
请注意:
JavaScript 从一开始就有了原型继承。这是 JavaScript 编程语言的核心特性之一。
但是在过去,没有直接对其进行访问的方式。唯一可靠的方法是本章中会介绍的构造函数的 "prototype" 属性。目前仍有许多脚本仍在使用它。
请注意,这里的 F.prototype 指的是 F 的一个名为 "prototype" 的常规属性。这听起来与“原型”这个术语很类似,但这里我们实际上指的是具有该名字的常规属性。
下面是一个例子:
let animal = {eats: true};function Rabbit(name) {this.name = name;}Rabbit.prototype = animal;let rabbit = new Rabbit("White Rabbit"); // rabbit.__proto__ == animalalert( rabbit.eats ); // true
设置 Rabbit.prototype = animal 的字面意思是:“当创建了一个 new Rabbit 时,把它的 [[Prototype]] 赋值为 animal”。
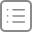
这是结果示意图:

在上图中,"prototype" 是一个水平箭头,表示一个常规属性,[[Prototype]] 是垂直的,表示 rabbit 继承自 animal。
F.prototype 仅用在 new F 时
F.prototype 属性仅在 new F 被调用时使用,它为新对象的 [[Prototype]] 赋值。
如果在创建之后,F.prototype 属性有了变化(F.prototype = <another object>),那么通过 new F 创建的新对象也将随之拥有新的对象作为 [[Prototype]],但已经存在的对象将保持旧有的值。
默认的 F.prototype,构造器属性
每个函数都有 "prototype" 属性,即使我们没有提供它。
默认的 "prototype" 是一个只有属性 constructor 的对象,属性 constructor 指向函数自身。
像这样:
function Rabbit() {}/* default prototypeRabbit.prototype = { constructor: Rabbit };*/

我们可以检查一下:
function Rabbit() {}// by default:// Rabbit.prototype = { constructor: Rabbit }alert( Rabbit.prototype.constructor == Rabbit ); // true
通常,如果我们什么都不做,constructor 属性可以通过 [[Prototype]] 给所有 rabbits 使用:
function Rabbit() {}// by default:// Rabbit.prototype = { constructor: Rabbit }let rabbit = new Rabbit(); // inherits from {constructor: Rabbit}alert(rabbit.constructor == Rabbit); // true (from prototype)

我们可以使用 constructor 属性来创建一个新对象,该对象使用与现有对象相同的构造器。
像这样:
function Rabbit(name) {this.name = name;alert(name);}let rabbit = new Rabbit("White Rabbit");let rabbit2 = new rabbit.constructor("Black Rabbit");
当我们有一个对象,但不知道它使用了哪个构造器(例如它来自第三方库),并且我们需要创建另一个类似的对象时,用这种方法就很方便。
但是,关于 "constructor" 最重要的是……
……JavaScript 自身并不能确保正确的 "constructor" 函数值。
是的,它存在于函数的默认 "prototype" 中,但仅此而已。之后会发生什么 —— 完全取决于我们。
特别是,如果我们将整个默认 prototype 替换掉,那么其中就不会有 "constructor" 了。
例如:
function Rabbit() {}Rabbit.prototype = {jumps: true};let rabbit = new Rabbit();alert(rabbit.constructor === Rabbit); // false
因此,为了确保正确的 "constructor",我们可以选择添加/删除属性到默认 "prototype",而不是将其整个覆盖:
function Rabbit() {}// 不要将 Rabbit.prototype 整个覆盖// 可以向其中添加内容Rabbit.prototype.jumps = true// 默认的 Rabbit.prototype.constructor 被保留了下来
或者,也可以手动重新创建 constructor 属性:
Rabbit.prototype = {jumps: true,constructor: Rabbit};// 这样的 constructor 也是正确的,因为我们手动添加了它
总结
在本章中,我们简要介绍了为通过构造函数创建的对象设置 [[Prototype]] 的方法。稍后我们将看到更多依赖于此的高级编程模式。
一切都很简单,只需要记住几条重点就可以清晰地掌握了:
F.prototype属性(不要把它与[[Prototype]]弄混了)在new F被调用时为新对象的[[Prototype]]赋值。F.prototype的值要么是一个对象,要么就是null:其他值都不起作用。"prototype"属性仅在设置了一个构造函数(constructor function),并通过new调用时,才具有这种特殊的影响。
在常规对象上,prototype 没什么特别的:
let user = {name: "John",prototype: "Bla-bla" // 这里没有魔法了};
默认情况下,所有函数都有 F.prototype = {constructor:F},所以我们可以通过访问它的 "constructor" 属性来获取一个对象的构造器。
任务
修改 “prototype”
重要程度: 5
在下面的代码中,我们创建了 new Rabbit,然后尝试修改它的 prototype。
最初,我们有以下代码:
function Rabbit() {}Rabbit.prototype = {eats: true};let rabbit = new Rabbit();alert( rabbit.eats ); // true
我们增加了一个字符串(强调)。现在
alert会显示什么?function Rabbit() {}Rabbit.prototype = {eats: true};let rabbit = new Rabbit();Rabbit.prototype = {};alert( rabbit.eats ); // ?
……如果代码是这样的(修改了一行)?
function Rabbit() {}Rabbit.prototype = {eats: true};let rabbit = new Rabbit();Rabbit.prototype.eats = false;alert( rabbit.eats ); // ?
像这样呢(修改了一行)?
function Rabbit() {}Rabbit.prototype = {eats: true};let rabbit = new Rabbit();delete rabbit.eats;alert( rabbit.eats ); // ?
最后一种变体:
function Rabbit() {}Rabbit.prototype = {eats: true};let rabbit = new Rabbit();delete Rabbit.prototype.eats;alert( rabbit.eats ); // ?
解决方案
答案:
true。Rabbit.prototype的赋值操作为新对象设置了[[Prototype]],但它不影响已有的对象。false。对象通过引用被赋值。来自
Rabbit.prototype的对象并没有被复制,它仍然是被Rabbit.prototype和rabbit的[[Prototype]]引用的单个对象。所以当我们通过一个引用更改其内容时,它对其他引用也是可见的。
true。所有
delete操作都直接应用于对象。这里的delete rabbit.eats试图从rabbit中删除eats属性,但rabbit对象并没有eats属性。所以这个操作不会有任何影响。undefined。属性
eats被从 prototype 中删除,prototype 中就没有这个属性了。
使用相同的构造函数创建一个对象
重要程度: 5
想象一下,我们有一个由构造函数创建的对象 obj —— 我们不知道使用的是哪个构造函数,但是我们想使用它创建一个新对象。
我们可以这样做吗?
let obj2 = new obj.constructor();
请给出一个可以使这样的代码正常工作的 obj 的构造函数的例子。再给出会导致这样的代码无法正确工作的例子。
解决方案
如果我们确信 "constructor" 属性具有正确的值,那么就可以使用这种方法。
例如,如果我们不触碰默认的 "prototype",那么这段代码肯定可以正常运行:
function User(name) {this.name = name;}let user = new User('John');let user2 = new user.constructor('Pete');alert( user2.name ); // Pete (worked!)
它起作用了,因为 User.prototype.constructor == User。
……但是如果有人,重写了 User.prototype,并忘记可重新创建 constructor 以引用 User,那么上面这段代码就会运行失败。
例如:
function User(name) {this.name = name;}User.prototype = {}; // (*)let user = new User('John');let user2 = new user.constructor('Pete');alert( user2.name ); // undefined
为什么 user2.name 是 undefined?
这是 new user.constructor('Pete') 的工作流程:
- 首先,它在
user中寻找constructor。没找到。 - 然后它追溯原型链。
user的原型是User.prototype,它也什么都没有。 User.prototype的值是一个普通对象{},该对象的原型是Object.prototype。并且Object.prototype.constructor == Object。所以就用它了。
最后,我们有 let user2 = new Object('Pete')。内建的 Object 构造函数会忽略参数,它总是创建一个类似于 let user2 = {} 的空对象,这就是最后我们在 user2 中拥有的东西。